Artificial Intelligence (AI) is revolutionising the way businesses operate, and at the forefront of this innovation are AI agents. These intelligent, autonomous systems are designed to streamline workflows, make informed decisions, and adapt to changing environments. In this blog, we’ll explore what AI agents are, their applications in various industries, and why investing in them can future-proof your business.
Topic Breakdown
What Are AI Agents?
AI agents are software programs capable of performing tasks autonomously. They perceive their environment, analyse data, and make decisions to achieve specific goals without constant human input. These agents are a combination of machine learning, natural language processing (NLP), and decision-making algorithms.
Types of AI Agents and Their Capabilities
AI agents come in various forms, each designed to handle different levels of complexity and decision-making. Understanding these types can help businesses choose the right AI solutions for their needs.
- Reactive Agents: The simplest form. They respond to real-time inputs without relying on memory, meaning they don’t learn from past experiences.
- Deliberative Agents: Plan and evaluate actions to make decisions.
- Learning Agents: Continuously improve over time using data and user interactions (learning patterns).
- Autonomous Agents: Operate independently, often across complex systems, adapting and optimising operations without external guidance.
Mapping Table
| AI Agent Type | AI Category | Key Capabilities | Example Use Cases |
| Reactive Agents | Reactive AI (Basic) | – Responds to current inputs only. – No memory, learning, or adaptation. | – Chess-playing AI (e.g., IBM’s Deep Blue). – Basic chatbots with pre-set responses. – AI-powered fraud detection that only flags rule-based anomalies. |
| Deliberative Agents | Limited Memory AI, Theory of Mind AI (Emerging) | – Evaluates multiple options before acting. – Uses historical data for better decisions. – Follows a Sense-Reason-Act cycle. | – Self-driving cars that analyze real-time traffic. – Strategic business decision AI that optimises workflows. – AI-powered customer support bots that adapt based on previous queries. |
| Learning Agents | Limited Memory AI, Theory of Mind AI (Future) | – Learns from past interactions. – Improves decision-making over time. – Uses machine learning or deep learning. | – Netflix & Spotify AI recommendations that refine suggestions based on user habits. – Fraud detection AI that evolves based on new patterns. – Siri & Alexa learning user preferences for smarter interactions. |
| Autonomous Agents | Self-Aware AI (Future), Limited Memory AI (Practical Today) | – Operates independently without human intervention. – Uses advanced learning, planning, and decision-making. – Can self-optimise based on external data. | – Autonomous drones for delivery. – Robo-advisors managing investments based on market trends and user goals. – Industrial robots in manufacturing that improve workflows on their own. |
Where Do We Stand Today?
- Reactive and Limited Memory AI are widely used in real-world applications.
- Theory of Mind AI is in early development, promising more intuitive human-AI interaction.
- Self-Aware AI remains theoretical but could redefine AI’s role in society in the future.

Applications in Business
AI-powered agents are transforming industries by automating repetitive tasks and enabling smarter decision-making. Here’s how businesses are leveraging them:
- Customer Support: AI-powered chatbots and virtual assistants handle customer queries, reducing response times and improving user experience. For example, intelligent agents can manage FAQs, process refunds, and offer personalised recommendations.
- E-commerce: AI software agents help with inventory management, dynamic pricing, and product recommendations, ensuring businesses stay competitive.
- Healthcare: These intelligent agents assist in diagnostics, patient monitoring, and scheduling appointments. They can analyse medical data faster than humans, improving outcomes. AI-driven health chatbots are now also gaining ground.
- Finance: Autonomous agents streamline processes like fraud detection, risk assessment, and algorithmic trading.
- Supply Chain Management: Smart AI assistants optimise logistics by predicting demand, automating inventory control, and ensuring timely deliveries.
Why Should Your Business Invest in AI Agents?
Adopting AI systems offers significant advantages for businesses in several key areas:
- Increased Efficiency 🚀: AI-powered agents streamline workflows by automating repetitive tasks, reducing manual effort, and optimizing processes. Businesses can eliminate bottlenecks and improve productivity by delegating tasks to AI-powered systems.
- Cost Savings 💰: AI automation helps businesses cut operational costs by reducing reliance on human labor for repetitive or time-consuming tasks. Through automation, companies can allocate resources more efficiently and lower expenses.
- Enhanced Customer Experience 🎯: Intelligent agents improve customer engagement by providing personalised interactions and instant support. Businesses that integrate AI into their customer service can build stronger relationships and boost retention rates.
- Data-Driven Decision Making 📊: AI agents process vast amounts of data quickly, uncovering insights that would take humans hours—or even days—to analyse. Businesses can leverage AI-driven analytics to make informed, strategic decisions.
- Competitive Advantage 🏆: Businesses that embrace AI agents gain an edge over competitors by leveraging automation, intelligence, and adaptability. As AI continues to evolve, companies that integrate AI early will lead their industries.
Challenges in Implementation
While AI agents offer numerous benefits, businesses must be aware of several challenges when implementing them. These challenges range from technical barriers to ethical concerns. Understanding these issues can help businesses develop a strategic approach to AI adoption while mitigating risks.
- Data Privacy & Security 🔐: AI agents rely on vast amounts of data to function effectively, making data privacy and security a top concern. Mishandling or unauthorized access to sensitive information can lead to data breaches, regulatory penalties, and loss of customer trust. Ensuring compliance with data protection laws like GDPR, CCPA, and Australia’s Privacy Act is crucial.
- Integration with Existing Systems ⚙️: Many businesses struggle to integrate AI agents into their current IT infrastructure. Legacy systems may not be compatible with AI-driven solutions, leading to inefficiencies, downtime, or the need for expensive system overhauls. Some AI solutions require cloud-based infrastructure, which businesses may not have in place. AI should work seamlessly with existing databases, ERPs, and CRM systems.
- Ethical Concerns & Bias in AI ⚖️: AI systems can inherit biases from the data they are trained on, leading to unfair or discriminatory outcomes. Businesses deploying AI must ensure ethical decision-making and fairness in AI-generated results.
- Cost & Resource Allocation 💰: Implementing AI agents requires significant investment in technology, infrastructure, and expertise. Businesses must carefully allocate resources to ensure a positive return on investment (ROI).
- Lack of Skilled Professionals 👨💻: AI implementation requires specialised knowledge in areas like machine learning, data science, and AI ethics. The global shortage of AI talent makes it difficult for businesses to find qualified professionals.
AI adoption is a strategic investment, and businesses must proactively address these challenges to ensure success. By prioritizing security, ethical considerations, cost management, and workforce readiness, organizations can unlock the full potential of AI agents without major disruptions. To address these challenges, working with a trusted technology partner is essential.
Real-World Examples
- AI in Healthcare – HealthTap 🏥: HealthTap’s AI-powered virtual assistant, Dr. A.I.™, conducts preliminary patient interviews before telemedicine consultations. This AI agent gathers patient information, analyzes symptoms, and provides doctors with relevant insights, allowing them to focus on diagnosis and treatment.
- AI in Smart Homes – Amazon Alexa🏠: Amazon’s Alexa is an AI-powered virtual assistant that responds to voice commands, controls smart home devices, and provides real-time information. It uses natural language processing (NLP) to understand and interact with users.
- AI in Finance – Wealthfront💰: Wealthfront uses robo-advisors powered by AI to provide automated investment management. These AI agents analyze market trends, assess risk tolerance, and create personalized investment portfolios without human intervention.
- AI in Transportation – Tesla Autopilot 🚗: Tesla’s Autopilot AI system is a prime example of an AI agent in autonomous driving. Using a combination of computer vision, deep learning, and real-time data processing, Tesla vehicles can drive semi-autonomously under specific conditions.
- AI in Software Development – OpenAI Codex 💻: OpenAI’s Codex, the AI model behind GitHub Copilot, helps software developers by automatically generating code snippets, suggesting improvements, and even completing entire functions based on natural language descriptions.
- AI in Entertainment – Spotify AI 🎵: Spotify’s AI-driven recommendation system personalizes playlists and suggests music based on user preferences, listening history, and even mood. The AI continuously adapts by learning from user interactions.
- AI in Customer Service – Google Duplex 📞: Google Duplex is an AI agent that can make phone calls, schedule appointments, and interact with businesses using natural human-like speech. It leverages deep learning and speech synthesis to create realistic conversations.
- AI in Enterprise Solutions – IBM Watson 🏢: IBM Watson’s AI-powered analytics assist businesses in decision-making, fraud detection, and customer engagement by analyzing large volumes of structured and unstructured data.
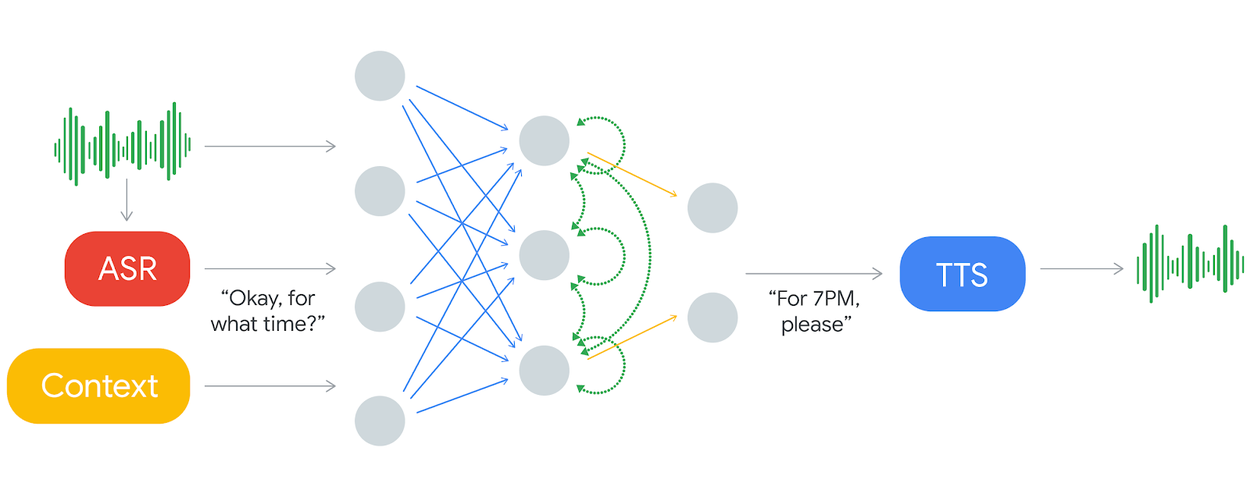
How to Get Started
Businesses should assess their needs before implementing AI agents. While Reactive and Limited Memory AI are currently the most applicable, advancements in AI technology may soon make Theory of Mind and Self-aware AI practical for real-world use. Here are steps to integrate AI agents into your business:
- Identify Processes to Automate: Focus on repetitive and time-consuming tasks.
- Choose the Right AI Solution: Select an AI agent tailored to your industry needs.
- Partner with Experts: Collaborate with an experienced AI development team to ensure a seamless implementation.
- Start Small, Scale Later: Begin with a pilot project and expand based on results.
FAQs
How do AI agents improve customer service?
AI-powered chatbots and virtual assistants provide instant responses, personalised recommendations, and 24/7 support, improving the overall customer experience.
Are AI agents expensive to implement?
While the initial investment can be high, the long-term benefits of efficiency and cost savings often outweigh the setup costs.
Can small businesses use AI agents?
Yes, AI agents are scalable and can be tailored to fit the needs and budgets of small businesses.
How do AI agents ensure data security?
Modern AI systems are built with advanced security measures like encryption and compliance with regulations to protect sensitive data.
Conclusion
AI agents are no longer just a futuristic concept; they are reshaping how businesses function across the globe. By integrating them into the workflow, businesses can achieve greater efficiency, accuracy, and scalability, staying competitive in today’s fast-paced market. Now is the time to embrace this technology and transform your operations for the future.
Ready to future-proof your business?